(A) RIGHT CIRCULAR CYLINDER:
A right circular cylinder is solid generated by the revolution of a rectangle about of its sides.
NOTE : If a paper, cylinder open at both the ends is cut along a vertical line on the curved surface and stretched on a plane surface, we obtain a rectangle of length i.e., 27πr and breadth= Height of cylinder h.
So, curved surface area (C.S.A) or lateral surface area = 2πr * height
So, curved surface area (C.S.A) or lateral surface area = 2πr * height
Important Formula For Cylinder
1. C. S. A of cylinder = ( Perimeter of base) * Height = 2πrh
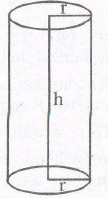
2. Area of each end of cylinder = 2πr2
3. Total surface area (including both circular ends) = 2πrh + 2πr2 = 27πr(h + r)
4. Volume of cylinder — πr2h = [(Area of base) * height]
Hollow Cylinder’s formulae e.g., (Rubber tubes pipes, etc.)
1. Volume of material = Exterior volume — Interior
volume = πR2h — πr2h = πh(R2 – r2)
volume = πR2h — πr2h = πh(R2 – r2)
2. C. S. A or L. S. A = external surface area + internal surface area
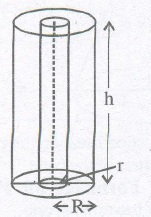
= 2πRh + 2πrh
3. T. S . A. of hollow cylinder = C. S. A+ 2 ( area of base ring )
= (2πRh + 2πrh) + 2(πR2 – πr2)
NOTE:
1. Two end faces of right circular cylinder are circles having each area = πr2
2. Mass of cylinder = Volume * density
3. When rectangular sheet of paper is rolled along its length , we get a cylinder whose base circumference is length of sheet and height is same as breadth of sheet.
(B) CONE
From figure, AO = height of cone and is denoted by ‘h’

OB = radius of the base of cone, AB = slant height of a cone (l)
Important Formula Of rt. Circular Cone :
1. Volume of cone = 1 / 3 πr2h
2 C. S. A or L. S. A=πrl where slant height
= l =√ r2 + hr2
3. T. S. A of cone = πrl + πr2
(C) FRUSTUM OF A CONE
FRUSTUM : A cone is cut by a plane parallel to the base of the cone,

then the portion between the plane and base is called frustum of the cone
Important Formulae for Frustum :
1. Volume of frustum of cone
= πh / 3[R2 + r2 + Rr] cubic unit
= πh / 3[R2 + r2 + Rr] cubic unit
2. L. S. A or C. S. A = πl(R + r) Sq units where l2 = h2 + (R – r)2
3. T. S. A = πR2 + πr2 + πl(R + r) Sq. units.
(Area of base + Area of top + Area of lateral )
(Area of base + Area of top + Area of lateral )
4. Slant height (l) = √h22 + (R – r)2
(D) IMPORTANT FORMULA FOR SPHERE AND HEW-SPHERE
(a) Surface area of sphere = 4πr2
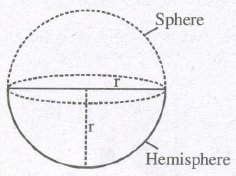
(b) Volume of sphere = 4 / 3 πr3
(c) Volume of hemisphere = 2 / 3 πr3
(d) C.S.A. of hemisphere = 2πr2
(e) Total surface area of Hemi-sphere = 2πr2+ πr2 =3πr2
(E) IMPORTANT FORMULA FUR SPHERICAL SHELL/ HEMILSPHERICAL SHELL
(a) Outer surface area of spherical shell =4πR2
(b) Inner S.A. of spherical shell = 4πr2
(c) Total surface area of spherical shell = 4π(R2+ r2)
(d) Volume of spherical shell of external radius R and internal
radius ‘r’ = 4 / 3π(R3 – r3)
(e) Outer curved surface area hemispherical shell = 2πR2
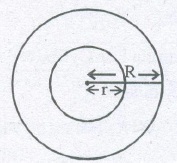
(f) Inner curved surface area of hemispherical shell = 2πr2
(g) Thick hemispherical bowl of external and internal radii R and r,
Total S.A. = π(3R2+ r2)
(h) Volume of hemispherical shell of external radius ‘R’ and internal radius ‘r’
= 2 / 3π(R3 — r2).
More chapters for class 10 maths


Post a Comment